Standardize naming, use spans and references for input parameters,
and improve documentation. Now the functions expect the lookups to
succeed as well, they will fail and assert otherwise.
The functions are also simple enough that it likely makes sense to keep
them all inlined
Strict compiler was generating possible-uninitialized warning.
Added an explicit initialization and asserts to solve the noisy
output and catch possible errors early on.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105990
Eager bounds calculation for cylindrical and spherical primitive nodes,
implemented in constant time rather than as a loop over all positions.
Takes into account the segments count of the circle from which they
are constructed. Solution of the task #105551.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105743
The Image node in the realtime compositor will output wrong passes if multiple passes are used at the same time. This is because images can only store a single layer, pass, and view at a time. Furthermore, they rely on operators and RNA callbacks to invalidate the cache when a different layer, pass, or view is requested. In effect, when the image node requests multiple passes at the same time without any kind of cache invalidation, wrong passes are output.
While a proper fix is to allow caching of multiple layers, passes, and views at the same time. This patch implements a temporary workaround by explicitly ensuring an up-to-date cache through a call to BKE_image_ensure_gpu_texture() when before requesting a GPU texture.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105547
Add `index_range()` and `is_empty()` functions, rename `ranges_num()`
to `size()` (clarifying the final extra integer as an implementation
detail). Also remove the `size(index)` function which gave almost the
same assembly as `[index].size()` (https://godbolt.org/z/PYzqYs3Kr).
Implements #102359.
Split the `MLoop` struct into two separate integer arrays called
`corner_verts` and `corner_edges`, referring to the vertex each corner
is attached to and the next edge around the face at each corner. These
arrays can be sliced to give access to the edges or vertices in a face.
Then they are often referred to as "poly_verts" or "poly_edges".
The main benefits are halving the necessary memory bandwidth when only
one array is used and simplifications from using regular integer indices
instead of a special-purpose struct.
The commit also starts a renaming from "loop" to "corner" in mesh code.
Like the other mesh struct of array refactors, forward compatibility is
kept by writing files with the older format. This will be done until 4.0
to ease the transition process.
Looking at a small portion of the patch should give a good impression
for the rest of the changes. I tried to make the changes as small as
possible so it's easy to tell the correctness from the diff. Though I
found Blender developers have been very inventive over the last decade
when finding different ways to loop over the corners in a face.
For performance, nearly every piece of code that deals with `Mesh` is
slightly impacted. Any algorithm that is memory bottle-necked should
see an improvement. For example, here is a comparison of interpolating
a vertex float attribute to face corners (Ryzen 3700x):
**Before** (Average: 3.7 ms, Min: 3.4 ms)
```
threading::parallel_for(loops.index_range(), 4096, [&](IndexRange range) {
for (const int64_t i : range) {
dst[i] = src[loops[i].v];
}
});
```
**After** (Average: 2.9 ms, Min: 2.6 ms)
```
array_utils::gather(src, corner_verts, dst);
```
That's an improvement of 28% to the average timings, and it's also a
simplification, since an index-based routine can be used instead.
For more examples using the new arrays, see the design task.
Pull Request: blender/blender#104424
Geometry Nodes: SDF Volume nodes milestone 1
Adds initial support for SDF volume creation and manipulation.
`SDF volume` is Blender's name of an OpenVDB grid of type Level Set.
See the discussion about naming in #91668.
The new nodes are:
- Mesh to SDF Volume: Converts a mesh to an SDF Volume
- Points to SDF Volume: Converts points to an SDF Volume
- Mean Filter SDF Volume: Applies a Mean Filter to an SDF
- Offset SDF Volume: Applies an offset to an SDF
- SDF Volume Sphere: Creates an SDF Volume in the shape of a sphere
For now an experimental option `New Volume Nodes` needs to be
enabled in Blender preferences for the nodes to be visible.
See the current work plan for Volume Nodes in #103248.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105090
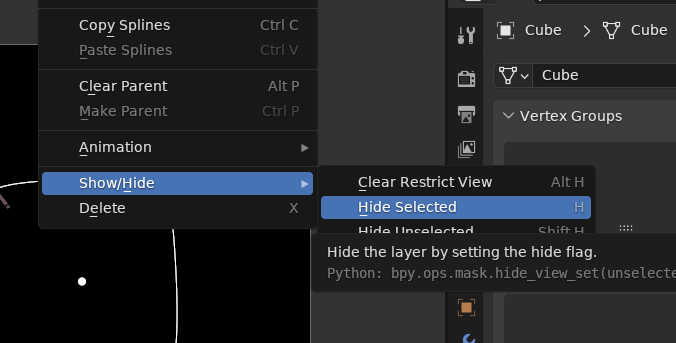
- Show/hide mask layers: the tooltip was confusing from a user's
perspective, because they should not be expected to know what a hide
flag is.
- Active Spline -> Active Point: likely a copy and paste error.
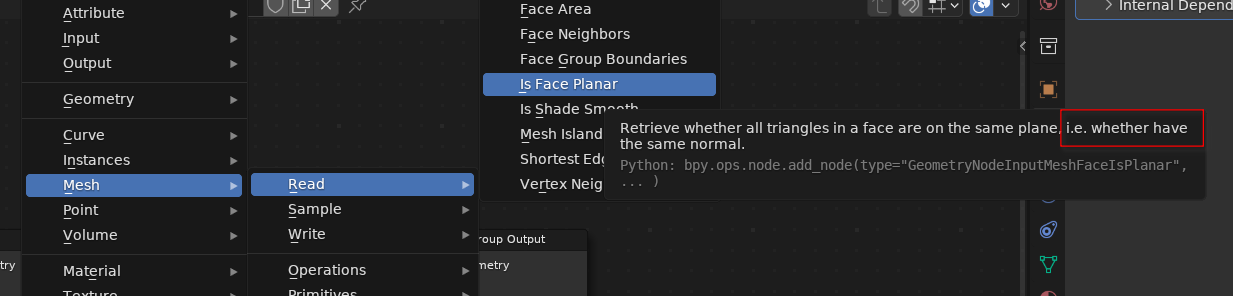
- Geo Nodes face is planar node: forgotten article.
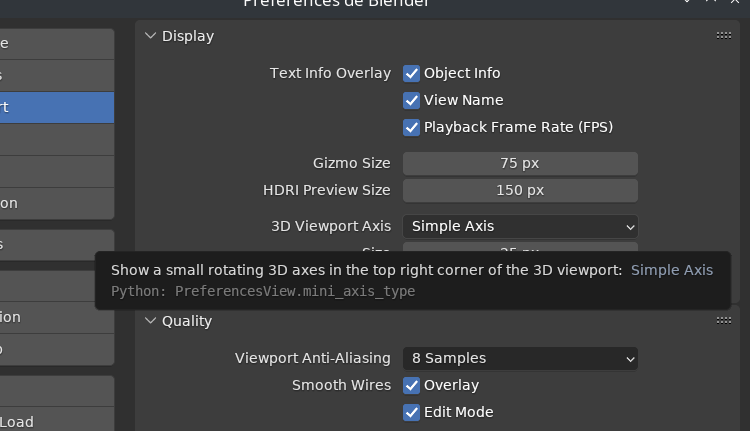
- Axes, plural instead of axis for the viewport preferences. Here
there are several usages of axis or axes. Since they refer to
coordinate axes I believe they should be plural, even though the
property `mini_axis_type` is still wrong.
-----
Pull Request: blender/blender#105814
Create GPUNodeLinks for tiled_image and tiled_image_mapping together, to ensure they are the same texture.
See blender/blender#105661 (comment) for context and a more in-depth explanation.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105772
... or carnidal interpolation with only 2 color stops.
This was triggering an incorrect path due to missing optimisation cases.
Just fall back to the unoptimized case fixes the assert.
This simplifies the usage of the API and is preparation for #104478.
The `CustomData_add_layer` and `CustomData_add_layer_named` now have corresponding
`*_with_data` functions that should be used when creating the layer from existing data.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105708
This changes the Switch node so that it is implemented directly as a lazy-function,
instead of as a normal geometry node which uses `GeoNodeExecParams`. This improves
the design of the layered execution api, where different nodes can be implemented
at a proper different abstraction level. The simplest kinds of nodes are implemented
as multi-function, then there is `GeoNodeExecParams` and more specialized nodes are
implemented as lazy-function. The switch node is special in the sense that it currently
needs extra behavior in the lazy-function graph generation anyway.
`GeoNodeExecParams` can be simplified as well, because the Switch node was the only
one that used the `lazy_` methods.
We could consider adding back lazy-input functionality to normal geometry nodes
as it becomes necessary. Ideally, that could be integrated with the node declaration.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105696
Refactoring mesh code, it has become clear that local cleanups and
simplifications are limited by the need to keep a C public API for
mesh functions. This change makes code more obvious and makes further
refactoring much easier.
- Add a new `BKE_mesh.hh` header for a C++ only mesh API
- Introduce a new `blender::bke::mesh` namespace, documented here:
https://wiki.blender.org/wiki/Source/Objects/Mesh#Namespaces
- Move some functions to the new namespace, cleaning up their arguments
- Move code to `Array` and `float3` where necessary to use the new API
- Define existing inline mesh data access functions to the new header
- Keep some C API functions where necessary because of RNA
- Move all C++ files to use the new header, which includes the old one
In the future it may make sense to split up `BKE_mesh.hh` more, but for
now keeping the same name as the existing header keeps things simple.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105416
The count wasn't clamped above zero in some newly optimized code.
Instead of adding it there, move the clamping to the field network,
similar to some other nodes. That makes it so the rest of the code
doesn't have to deal with the clamping, and should be faster in the
single-value case.
For mesh primitives, the bounds can be calculated trivially in advance
with negligible cost. In case they are needed later on, setting them
eagerly can save the calculation later on. For large meshes, this can
save tens of milliseconds before drawing.
Pull Request: blender/blender#105266
Invalid nodes are not added to the lazy-function graph. Therefore, their
outgoing links are also not added, which implies that the targets need
some default value.
Currently the shade smooth status for mesh faces is stored as part of
`MPoly::flag`. As described in #95967, this moves that information
to a separate boolean attribute. It also flips its status, so the
attribute is now called `sharp_face`, which mirrors the existing
`sharp_edge` attribute. The attribute doesn't need to be allocated
when all faces are smooth. Forward compatibility is kept until
4.0 like the other mesh refactors.
This will reduce memory bandwidth requirements for some operations,
since the array of booleans uses 12 times less memory than `MPoly`.
It also allows faces to be stored more efficiently in the future, since
the flag is now unused. It's also possible to use generic functions to
process the values. For example, finding whether there is a sharp face
is just `sharp_faces.contains(true)`.
The `shade_smooth` attribute is no longer accessible with geometry nodes.
Since there were dedicated accessor nodes for that data, that shouldn't
be a problem. That's difficult to version automatically since the named
attribute nodes could be used in arbitrary combinations.
**Implementation notes:**
- The attribute and array variables in the code use the `sharp_faces`
term, to be consistent with the user-facing "sharp faces" wording,
and to avoid requiring many renames when #101689 is implemented.
- Cycles now accesses smooth face status with the generic attribute,
to avoid overhead.
- Changing the zero-value from "smooth" to "flat" takes some care to
make sure defaults are the same.
- Versioning for the edge mode extrude node is particularly complex.
New nodes are added by versioning to propagate the attribute in its
old inverted state.
- A lot of access is still done through the `CustomData` API rather
than the attribute API because of a few functions. That can be
cleaned up easily in the future.
- In the future we would benefit from a way to store attributes as a
single value for when all faces are sharp.
Pull Request: blender/blender#104422
In order to properly translate UI messages, they sometimes need to be
disambiguated using translation contexts. Until now, node sockets had
no way to specify contexts and collisions occurred.
This commit adds a way to declare contexts for each socket using:
`.translation_context()`
If no context is specified, the default null context is used.
Pull Request #105195
The current API makes more sense as part of a class, but for now, keep
consistency with the other geometry module headers and move the code
to the proper namespace, removing the `GEO_` prefix which is only meant
for C code.
Pull Request #105357
With the goal of clearly differentiating between arrays and single
elements, improving consistency across Blender, and using wording
that's easier to read and say, change variable names for Mesh edges
and polygons/faces.
Common renames are the following, with some extra prefixes, etc.
- `mpoly` -> `polys`
- `mpoly`/`mp`/`p` -> `poly`
- `medge` -> `edges`
- `med`/`ed`/`e` -> `edge`
`MLoop` variables aren't affected because they will be replaced
when they're split up into to arrays in #104424.
As part of #95966, move the `ME_SEAM` flag on mesh edges
to a generic boolean attribute, called `.uv_seam`. This is the
last bit of extra information stored in mesh edges. After this
is committed we can switch to a different type for them and
have a 1/3 improvement in memory consumption.
It is also now possible to see that a mesh has no UV seams in
constant time, and like other similar refactors, interacting with
only the UV seams can be done with less memory.
The attribute name starts with a `.` to signify that the attribute,
like face sets, isn't meant to be used in arbitrary procedural
situations (with geometry nodes for example). That gives us more
freedom to change things in the future.
Pull Request #104728
Consistent with naming from 1af62cb3bf. Keep the "coord"
naming in the "vert_coords_alloc" set of functions since they should be
removed (see #103789).
Share the bounds cache across the input and output meshes of some
mesh operations that don't change the min and max positions: simple
subdivision, edge/face deletion, and triangulation. If the source mesh's
bounds are computed, or if the mesh is persistent, this can save
recalculation of the bounding box, which takes a few milliseconds
for large meshes.
In Edges and Edges & Faces modes, the node copied the positions once
with the other generic attributes and another time specifically just as
the positions. This is now unnecessary since positions are stored as
a generic attribute (1af62cb3bf). In a simple test this saved
2ms out of a total 12 in these modes.
66dda2b902 made an incorrect change to account for the special
case for NURBS. Instead, make the step that turns the lengths into
parameters more explicit, and pass the correct total length for each
curve, even in the cyclic case.
Pull Request #105079
Do the domain check directly in the field input class to avoid the need
for another function to do it elsewhere. Also move one function to
be closer to a similar one, rename some functions, and avoid the need
for two intermediate span variables.
Add a per node type callback for creating node add search operations,
similar to the way link drag search is implemented (11be151d58).
Currently the searchable strings have to be separate items in the list.
In a separate step, we can look into adding invisible searchable text
to search items if that's still necessary.
Resolves#102118
Pull Request #104794